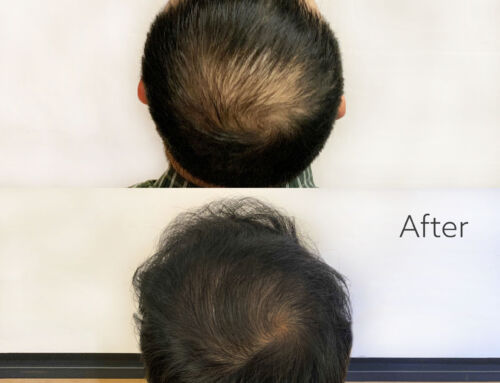
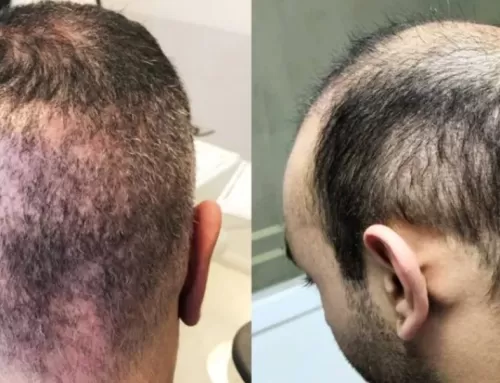
A hair transplant can completely change a man’s life, boosting his self-image and giving him greater confidence than he has enjoyed in years. Like many patients, you may think that hair transplants sound too good to be true. Could there finally be a solution for baldness that works? There have to be some major drawbacks and side effects, right? Actually, hair transplants are safe and effective. At our Boston practice, the most common side effect we see among hair transplants patientsis itching. Fortunately, this side effect is temporary and is typically very easy to treat.
A Quick Run Down of Hair Transplants
We use two techniques for surgical hair loss treatment, although both work similarly. In Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), we remove individual hair follicles from the donor site, located on the back of your head. This technique involves minimal tissue removal, since we must only remove the skin immediately around the individual hair. This area is typically less than a millimeter in diameter. Then we will place the individual hair follicles in the treatment area, where they will begin to grow naturally. An alternative method is Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT). To perform this technique, we will remove a narrow piece of tissue from the back of the head, carefully preserving and isolating individual follicles. Then we will graft the entire piece of tissue onto the treatment area.
What Causes Post-Operative Itching?
Itching can be caused by several factors. The most common cause is simply the healing process. As donor sites begin to heal, they will scab over, leaving you with an itchy, tingly feeling in that area. Other, less common reasons you may experience itching include:
- Dryness, especially from shampooing
- An allergic reaction to topical ointments
- An infection
- A pre-existing skin condition
How to Control and Treat Itching
While itching is not dangerous (except in the very rare cases when it is caused by infection), it can be very irritating. We use meticulous surgical techniques for male hair transplantation to avoid excess scabs and crusting during recovery. We provide topical ointments to treat any residual itching that remains. You may also find anti-histamines, petroleum jelly, and baby oil to be effective. Additionally, medicated shampoo may help to remove scabs and control itching. This prickly feeling can occur for up to three months following your hair transplant surgery. During the first month, you should avoid scratching your head and irritating the healing tissues. However, after that initial period, gentle massages may help the itching and stimulate healing.
Other Potential Side Effects
There are several common side effects that often accompany itching, including:
- Mild swelling: This effect usually dissipates within five days of your hair transplant.
- Bruising: This, too, usually disappears within a few days, and it can often be concealed by wearing a baseball cap.
- Pimples: This side effect is actually a sign of hair follicle activity below the scalp. Pimples should disappear at about the same time as the itchiness. You should note, however, that if the pimples are severe, it could be a sign of infection and you should alert your doctor.
Our Surgeons Use Advanced Techniques to Minimize Side Effects
With our careful, advanced surgical techniques, we work to reduce your risk for post-procedural itchiness and irritation. To learn more about our surgical processes and how to treat itchiness after your hair transplant, schedule a virtual consultation with NE Hair today.
COVID-19 Update
We are offering an initial hair transplant for the incredible price of $6,000, call 800-313-HAIR or click here to learn more.