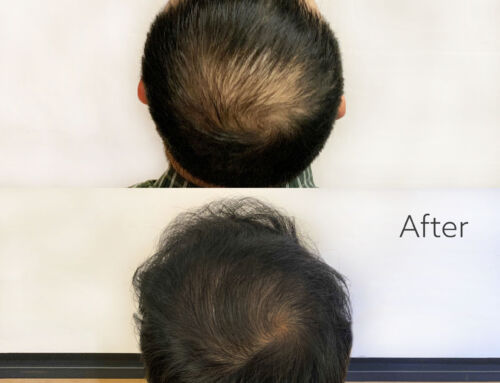
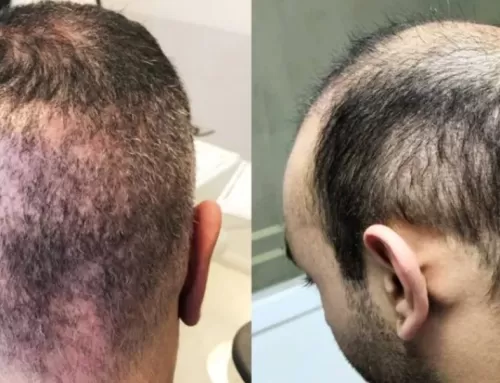
Patients throughout the greater Boston area know that they can count on the New England Center for Hair Restoration. They offer the latest in hair transplant surgery as well as non-surgical hair loss treatment, both of which can effectively treat balding and hair thinning.
A popular non-surgical treatment that helps many people experiencing hair loss is Rogaine, which is a well-known brand name for the drug minoxidil. Let’s look at minoxidil in more detail right now.
About Rogaine (Minoxidil)
Minoxidil is a popular topical drug that’s used to stimulate hair growth and slow down the process of balding/hair loss. While minoxidil will not cure balding per se, it can help reduce the appearance and noticeability of the hair loss that a person experiences.
How Rogaine (Minoxidil) Works
Minoxidil works by enlarging hair follicles and thereby extending the growth phase of the follicle. The drug also promotes additional blood flow to the scalp, which helps stimulate the growth of hair from the hair follicles.
Minoxidil is usually applied topically twice a day, with patients using special applicators or application techniques based on their needs. Patients should follow all label instructions carefully as well as any recommendations from their hair loss specialist. These will help prevent adverse side effects or complications.
There are different concentrations of minoxidil available, typically 2% and 5%.
Ideal Candidates for Rogaine (Minoxidil)
The best candidates for minoxidil are people who are experiencing early stages of hair loss. Young men in their 20s prove to be very good candidates as minoxidil is able to help prevent more significant balding with time. It’s important that anyone considering minoxidil use consult with their general physician as well as a hair loss specialist before initiating treatment.
Can women use Rogaine (minoxidil) for their hair loss?
Yes.
Women who are experiencing hair loss related to menopause or other hormonal changes are potentially good candidates for minoxidil. In most cases, women use the 2% minoxidil formula rather than the 5% formula.
If a woman is pregnant or nursing, it’s a good idea to avoid initiating minoxidil treatment until after pregnancy and breastfeeding simply to ensure the safety and wellness of the baby.
How does Rogaine (Minoxidil) compare to Propecia (Finasteride)?
In general, Propecia (finasteride) can be more effective when treating certain cases of baldness since it inhibits DHT rather than just stimulating hair growth. Propecia is an oral medication rather than a topical one.
That said, combining minoxidil with finasteride can result in reduced hair loss and significant hair regrowth, resulting in a effective treatment for balding without the need for surgery.
How does Rogaine (Minoxidil) compare to hair restoration surgery?
Hair restoration surgery offers exceptional results as well as natural-looking hair that grows when transplanted to the bald area.
In some ways these two treatments are not necessarily comparable since they accomplish different tasks, and each does their respective task well. You hair restoration specialist can go over the pros and cons of these treatments in more detail during a consultation so you can determine which one is better for you and your needs.
Contact Our Hair Loss and Restoration Specialists
For more information about Rogaine and your other options for treating hair loss and male pattern balding, be sure to contact our hair restoration specialists today. The team at New England Center for Hair Restoration look forward to your visit and helping you achieve a full and healthy head of hair.