Male pattern baldness, also known as androgenic alopecia (AGA), is a common condition affecting millions of men worldwide. Characterized by a receding hairline or thinning at the crown, AGA can progress to complete baldness on top of the scalp, leaving only a ring of hair around the sides. Thanks to advancements in hair restoration, today’s treatments offer both scientific precision and artistic finesse to help men regain their natural look—and their confidence.
Understanding Male Pattern Baldness
Male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a condition that affects millions of men globally. Characterized by a receding hairline and thinning hair on the crown, it can progress to more extensive hair loss if left untreated. This type of hair loss is primarily driven by genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors.
The condition is hereditary, meaning it can be passed down from either parent. If you have a family history of baldness, you are more likely to experience it yourself. Symptoms can vary, but common signs include thinning hair on the scalp, a receding hairline, and hair loss on the crown and temples.
Early diagnosis is crucial for managing male pattern baldness effectively. A doctor can diagnose the condition through a physical examination and medical history. In some cases, a scalp biopsy may be performed to rule out other causes of hair loss.
Hair Growth and Hair Follicles
Hair growth is a fascinating and complex process involving various cell types, hormones, and growth factors. At the heart of this process are hair follicles, the tiny structures in the skin of the scalp responsible for producing hair.
Each hair follicle consists of several layers of cells, including the dermal papilla, the hair shaft, and the sebaceous gland. The dermal papilla, located at the base of the follicle, plays a crucial role in producing the hair shaft, which is the visible part of the hair made of keratin. The sebaceous gland produces sebum, an oily substance that keeps the hair and scalp healthy.
Hair growth occurs in three distinct phases: anagen, catagen, and telogen. The anagen phase is the active growth phase, during which hair grows rapidly. The catagen phase is a short transitional period where hair growth slows down. Finally, the telogen phase is the resting phase, during which the hair is released from the follicle and eventually falls out.
What Causes AGA in Men?
AGA is driven by a combination of genetic predisposition and the effects of androgens, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT causes susceptible hair follicles to shrink, leading to shorter, finer hair until eventually, the follicles stop producing new hair. Age and stress can accelerate this process, but the primary cause remains hereditary.
Androgens stimulate hair growth in certain areas of the body such as the beard and axillary regions, while simultaneously suppressing hair growth on the frontal scalp in genetically predisposed individuals.
“The role of DHT is central to hair loss,” says Dr. Welter, a specialist in hair restoration. “Men who are genetically sensitive to DHT will see progressive thinning, particularly at the temples and crown.”
Fortunately, the field of hair restoration has come a long way from the clunky procedures of the past. Modern treatments address both the underlying causes and cosmetic concerns associated with male pattern baldness.
The Science of Hair Loss
Hair loss is a multifaceted process influenced by genetics, hormones, and environmental factors. Male pattern baldness, or androgenetic alopecia, is primarily caused by the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a potent form of testosterone.
DHT binds to androgen receptors in hair follicles, causing them to shrink over time. This process, known as miniaturization, leads to shorter, finer hair until the follicles eventually stop producing new hair altogether. The progression of hair loss is gradual, often taking several years to become noticeable.
Other factors can also contribute to hair loss, including stress, poor diet, and certain medical conditions. Stress can increase cortisol production, disrupting the normal hair growth cycle. A diet lacking essential nutrients like iron and biotin can weaken hair, while conditions such as thyroid disease and autoimmune disorders can also lead to hair loss.
Symptoms and Stages of Male Pattern Baldness
Male pattern baldness is a progressive condition that can be classified using the Norwood scale, a widely recognized system that describes its stages. Understanding these stages can help you identify the extent of your hair loss and seek appropriate treatment.
- Stage I: Minimal hair loss with a slight recession of the hairline.
- Stage II: Moderate hair loss with a noticeable recession of the hairline.
- Stage III: Significant hair loss with a balding spot on the crown.
- Stage IV: Advanced hair loss with a larger balding spot on the crown.
- Stage V: Severe hair loss with a large balding spot and a receding hairline.
- Stage VI: Very severe hair loss with extensive balding on the crown and a receding hairline.
- Stage VII: Extensive hair loss with complete baldness on the top of the head.
Recognizing these stages can help you and your doctor develop a tailored treatment plan to manage your hair loss effectively.
The Evolution of Hair Transplants: From Plugs to Precision
If you think of old hair transplant techniques, you might recall images of high-profile figures like Joe Biden during the 1980s, with hair clumps arranged in neat, grid-like rows. “Back then, transplants were like planting orchards,” Dr. Welter explains. “But today, we transplant individual hairs with the same precision as planting rice paddies.”
Modern hair transplantation procedures focus on the safe donor zone—the area at the back of the scalp where hair follicles are genetically resistant to male pattern baldness. These hairs are extracted and meticulously placed in thinning areas to replicate the patient’s natural hair growth pattern. Techniques such as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) have proven effective in surgical restoration of hair loss.
“The artistry of hair restoration is all about randomizing the placement,” says Dr. Welter. “Random patterns make the difference between a natural and artificial appearance.”
For men of different ethnic backgrounds, hair density and texture play a crucial role in achieving optimal results. For example, African American men may achieve better coverage with fewer hairs due to their naturally curly hair structure. In contrast, men with fine, straight hair may require denser transplants to create the same visual effect.
Diagnosis and Early Detection
Early diagnosis is key to managing male pattern hair loss effectively. Dermatologists typically assess the pattern and severity of hair thinning during a scalp examination. Blood tests may also be performed to rule out other causes, such as nutritional deficiencies or thyroid imbalances.
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, female androgenic alopecia affects around 30 million women in the United States, with an increasing occurrence at earlier ages and significant psychological impact.
“By the time I noticed my crown thinning, I thought it was too late,” shares John, a 39-year-old software engineer. “But after starting treatment with finasteride, I’ve seen new hair growth in just a few months.”
Treatment Options for Androgenetic Alopecia
Men have more options than ever to slow hair loss, stimulate regrowth, and restore their natural hairlines. Here’s a closer look at the most effective solutions:
Various treatments for androgenetic alopecia have shown potential for hair regrowth, with medications like minoxidil and finasteride demonstrating efficacy in empirical studies.
1. Finasteride (Propecia)
Finasteride remains a cornerstone of hair preservation. By blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT, this prescription medication helps prevent further hair loss and may even encourage regrowth in thinning areas. Finasteride can also help prevent permanent hair loss by addressing conditions like androgenetic alopecia, which primarily impacts the hair follicles and can lead to irreversible changes unless treated early.
“You can’t get blood from a stone,” Dr. Welter warns. “Some pre-existing hair must remain in the area for Propecia to work.”
2. Minoxidil (Rogaine)
This over-the-counter topical treatment prolongs the growth phase of hair follicles and increases blood flow to the scalp. Regular application is crucial to maintain results.
“After six months of minoxidil, I saw my bald spot shrink,” says Mike, a 42-year-old fitness instructor. “It’s part of my daily routine now.”
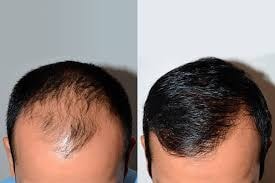
3. Hair Transplants
Modern hair transplant surgery procedures have evolved significantly from the early days of plug-like rows. Today’s techniques, including Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Strip Surgery (FUSS), focus on precision and artistry to achieve a natural look.
- FUE involves extracting individual hair follicles from the safe donor zone at the back of the scalp. The follicles are implanted into tiny incisions in thinning areas, resulting in minimal scarring and a quicker recovery.
- FUSS removes a strip of scalp, from which multiple follicular units are harvested and implanted. While this method may leave a linear scar, it can be a more efficient option for those needing extensive coverage.
“Transplants today are like planting individual seeds,” explains Dr. Welter, a hair restoration specialist. “The key is randomizing the placement to mimic natural hair patterns.” After surgery, most patients return to work within a few days. New hair begins to grow within a few months, with full results appearing after six to nine months.
“Getting a transplant was the best decision I’ve made for my confidence,” says Aaron, a 43-year-old entrepreneur. “I look like myself again, and people notice.”
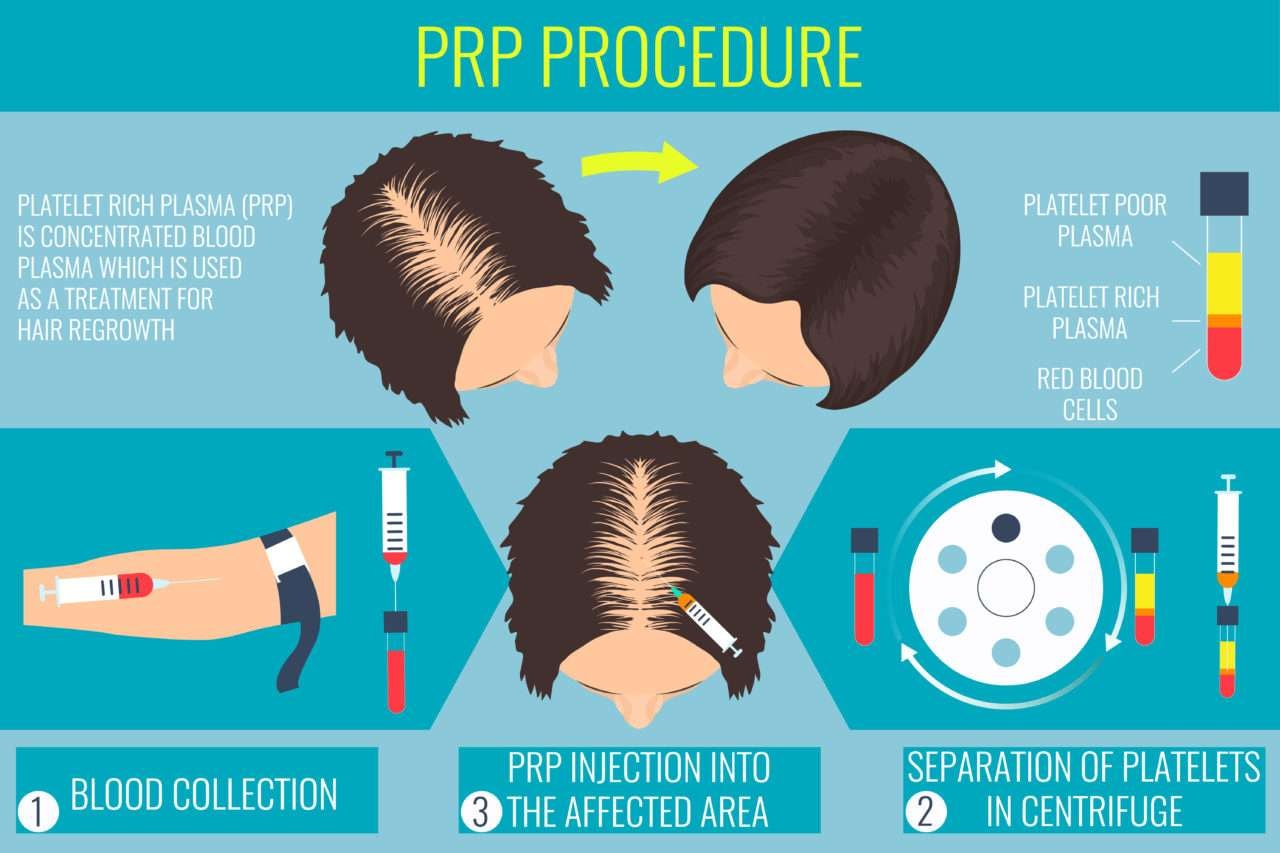
Innovative Therapies: PRP and Low-Level Laser Therapy
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves injecting concentrated growth factors from the patient’s own blood into the scalp. This stimulates dormant hair follicles and accelerates regrowth.
“Growth factors are the secret sauce in PRP therapy,” says Dr. Welter. “With advancements, results now appear in as little as six months.”
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
LLLT uses red light wavelengths to stimulate follicular activity, reducing hair loss and promoting density. Devices like laser combs and caps are convenient for at-home use.
“I was skeptical about laser therapy at first,” admits Eric, a 28-year-old accountant. “But after three months of consistent use, I noticed less shedding and thicker hair.”
Lifestyle Changes and Preventative Care
Preventative measures can also play a role in preserving hair:
- Nutrition: Eating a balanced diet rich in biotin, zinc, and iron supports hair health.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress may contribute to hair thinning. Techniques like meditation and exercise can reduce its impact.
- Gentle Hair Care: Avoiding harsh chemical treatments and excessive heat can protect the integrity of your hair.
It’s important to recognize that different types of hair loss require tailored treatments. Some conditions may even allow for natural regrowth without intervention, while others might need specific medications or surgical options.
Preparing for Your Appointment
If you’re experiencing hair loss, consulting a doctor is a crucial step in determining the underlying cause and exploring treatment options. Here are some tips to help you prepare for your appointment:
- List Your Symptoms: Note when your hair loss started and how long it has lasted.
- Medical History: Write down any underlying conditions that may be contributing to your hair loss.
- Questions for Your Doctor: Prepare questions such as “What is causing my hair loss?” and “What are my treatment options?”
- Diet and Hair Care Routine: Be ready to discuss your diet, hair care habits, and family history.
- Visual Evidence: If possible, bring a picture of your hair loss to show your doctor.
Being well-prepared for your appointment can help your doctor diagnose the cause of your hair loss and develop an effective treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Success Stories and Renewed Confidence
For many men, the journey to reclaiming their hair is also a journey to rediscovering their confidence.
“After combining finasteride, PRP therapy, and a hair transplant, I feel like I’ve turned back the clock,” shares Dave, a 45-year-old entrepreneur. “I’m not just seeing more hair—I’m seeing more of myself in the mirror.”
Hair restoration today merges scientific advancements with artistic mastery. Whether you’re exploring medications, surgical options, or supportive therapies, a personalized approach can yield life-changing results.
Take the First Step
If you’re noticing thinning or shedding, now is the time to take action. Early intervention can make all the difference in managing male pattern hair loss. Consult a hair specialist to create a tailored treatment plan that fits your needs.
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. With modern techniques, expert care, and a little patience, you can achieve a natural, healthy hairline—and a renewed sense of confidence.